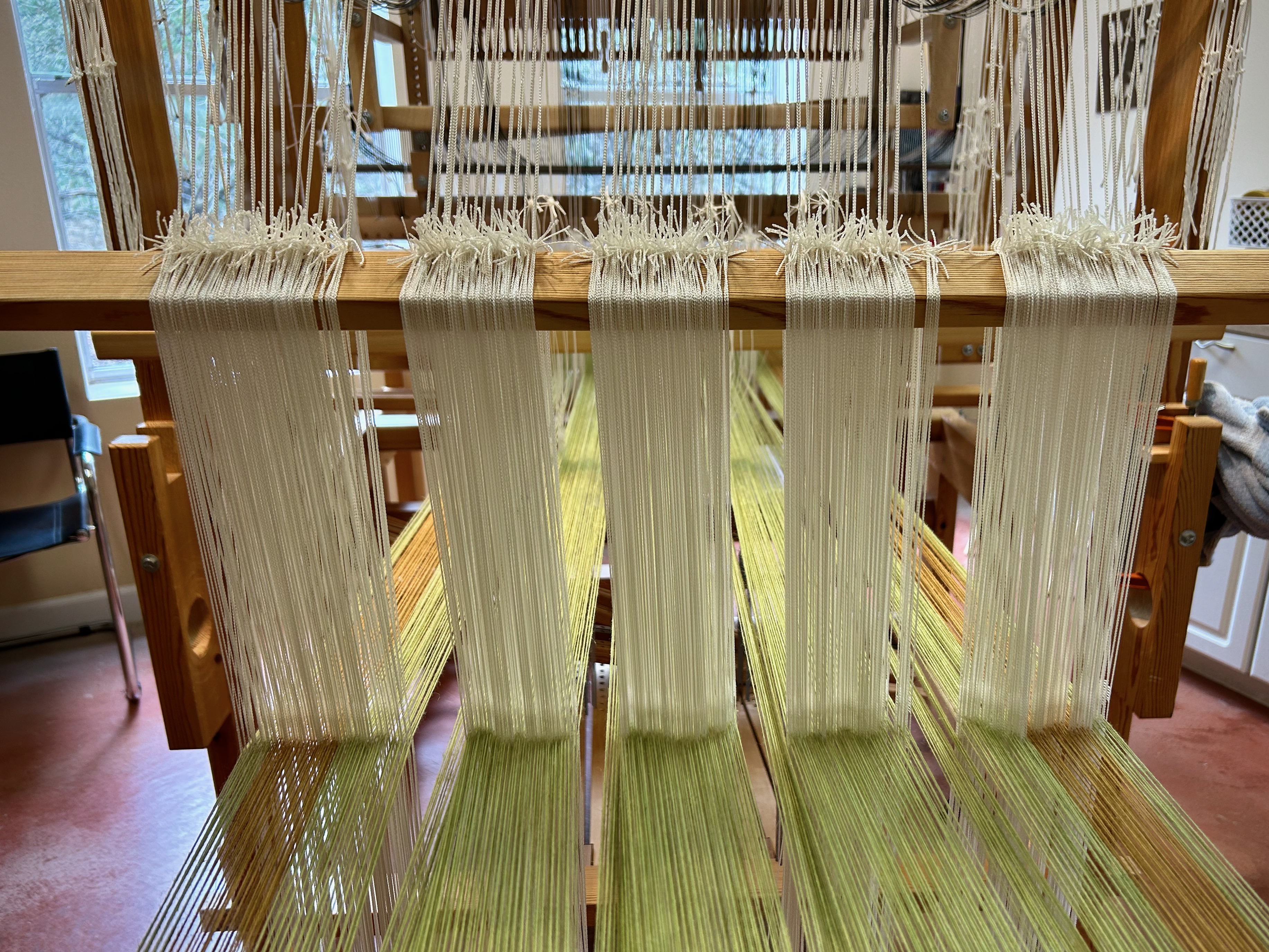
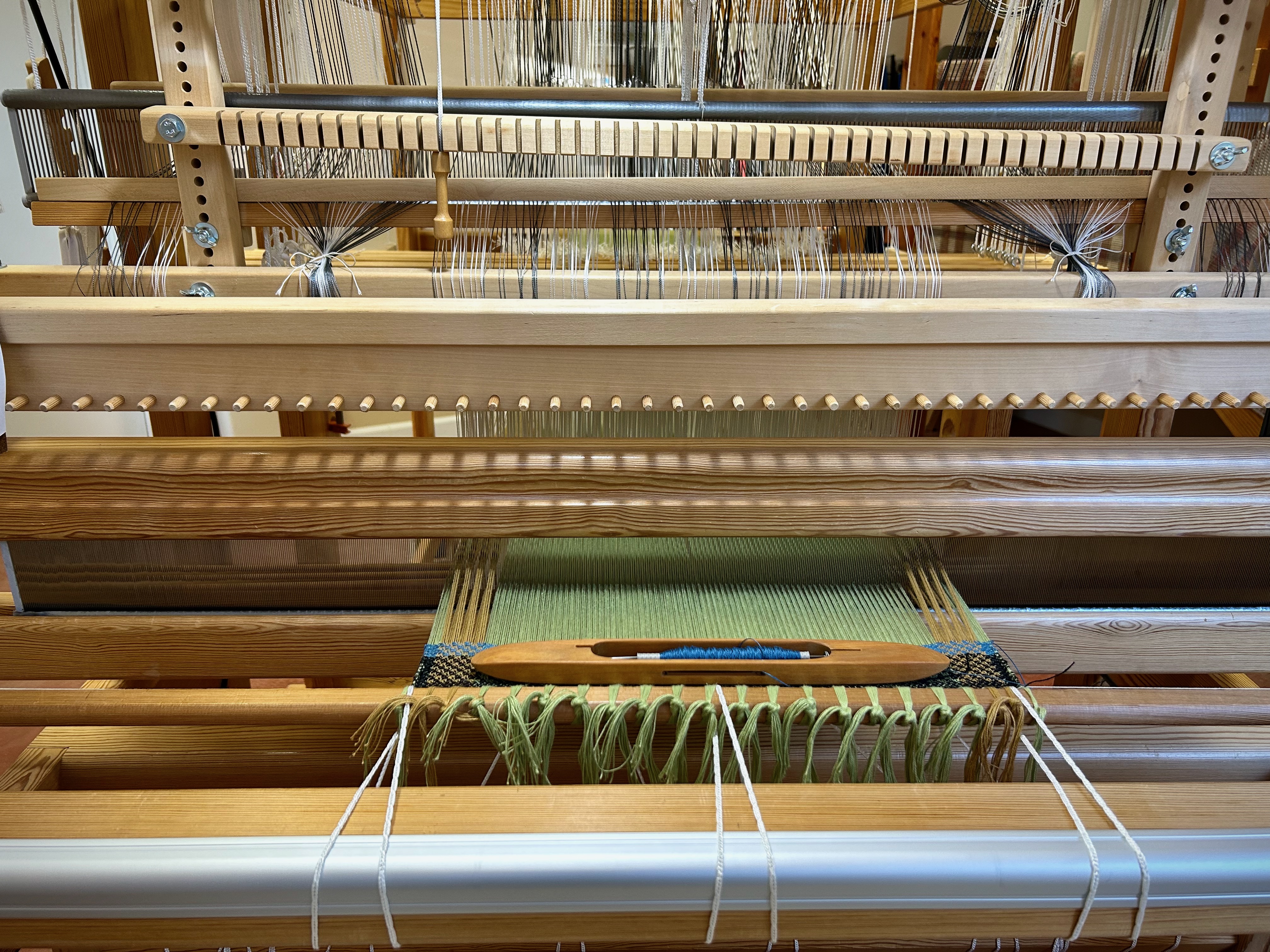
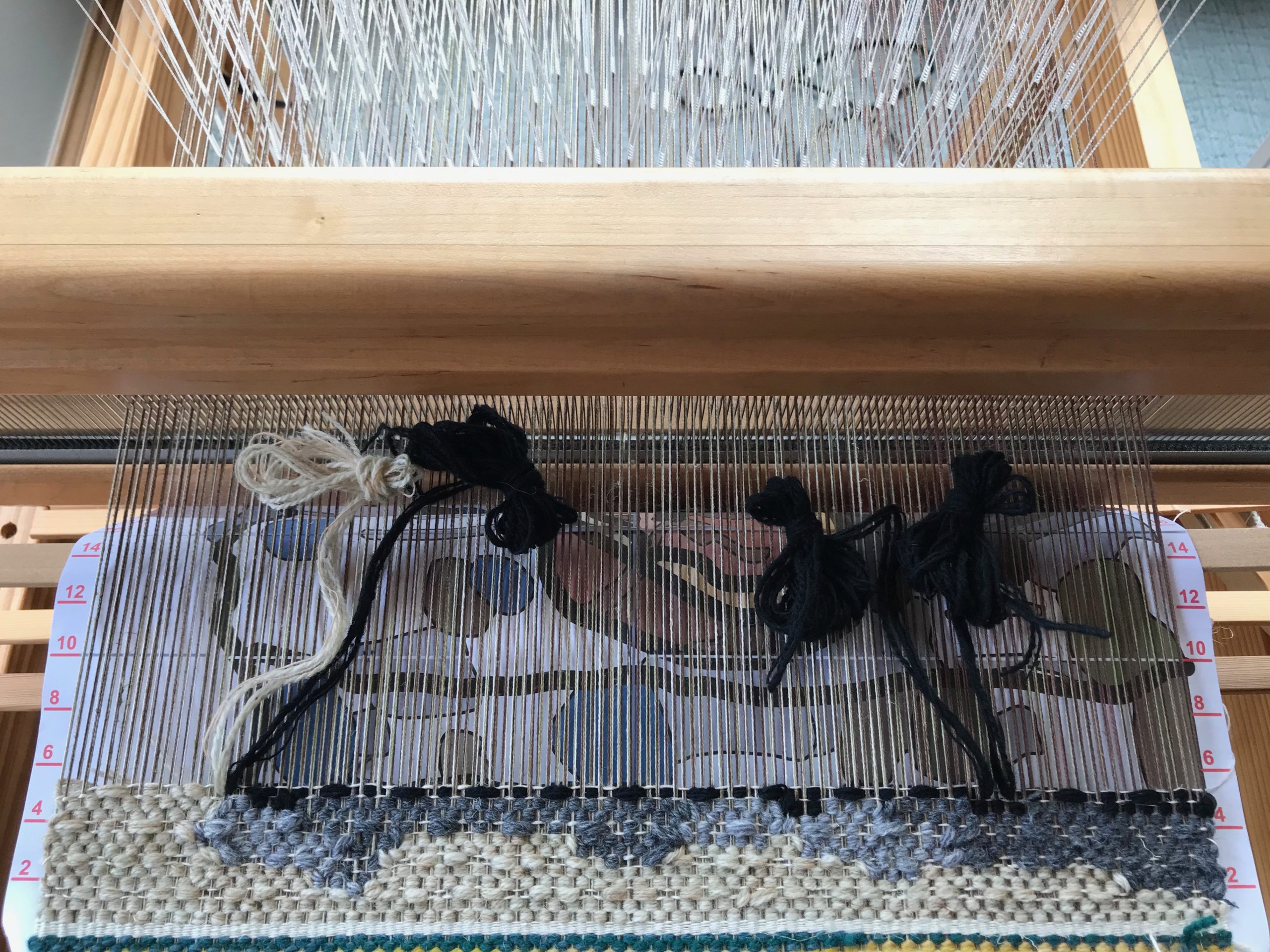
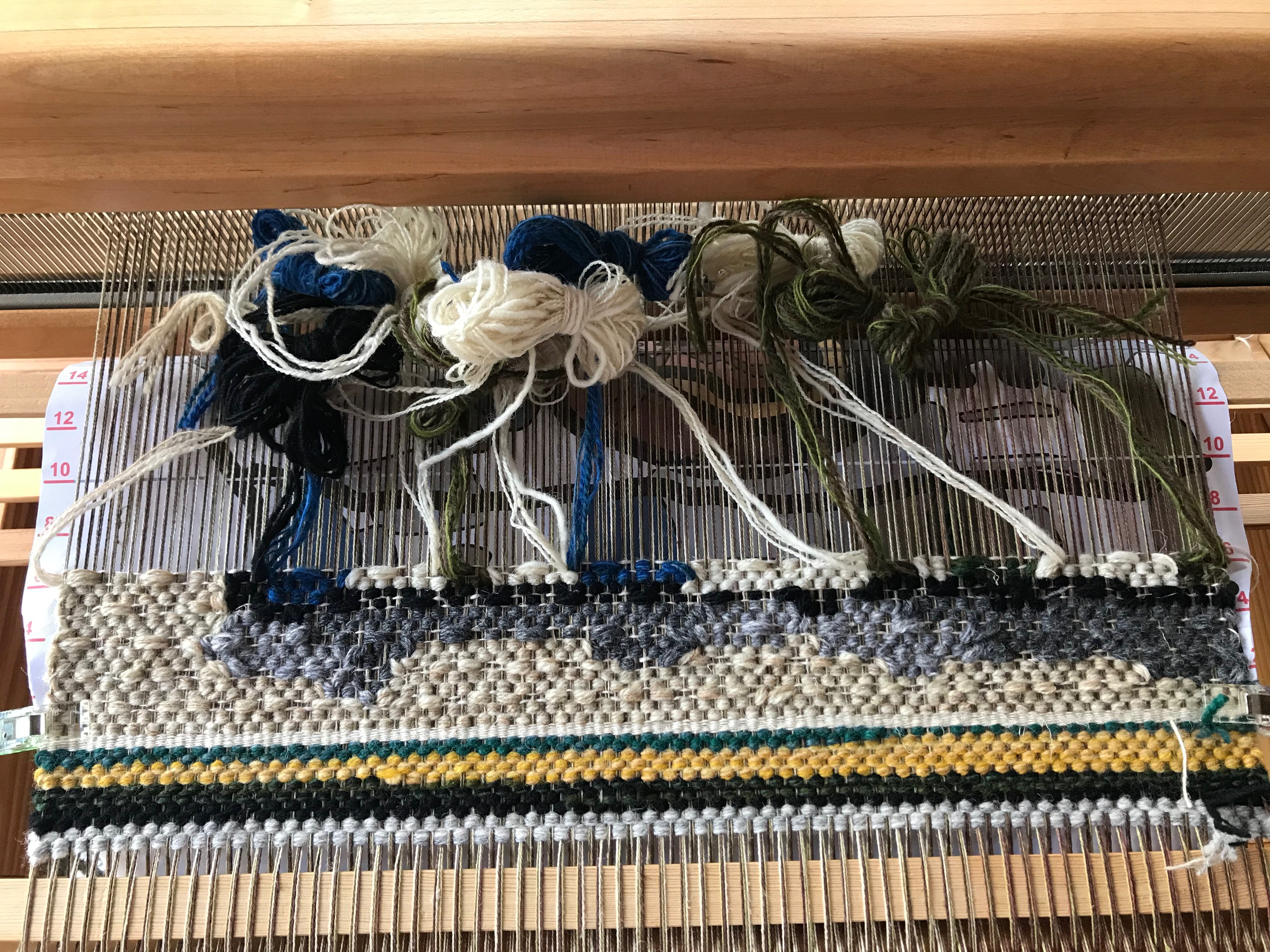
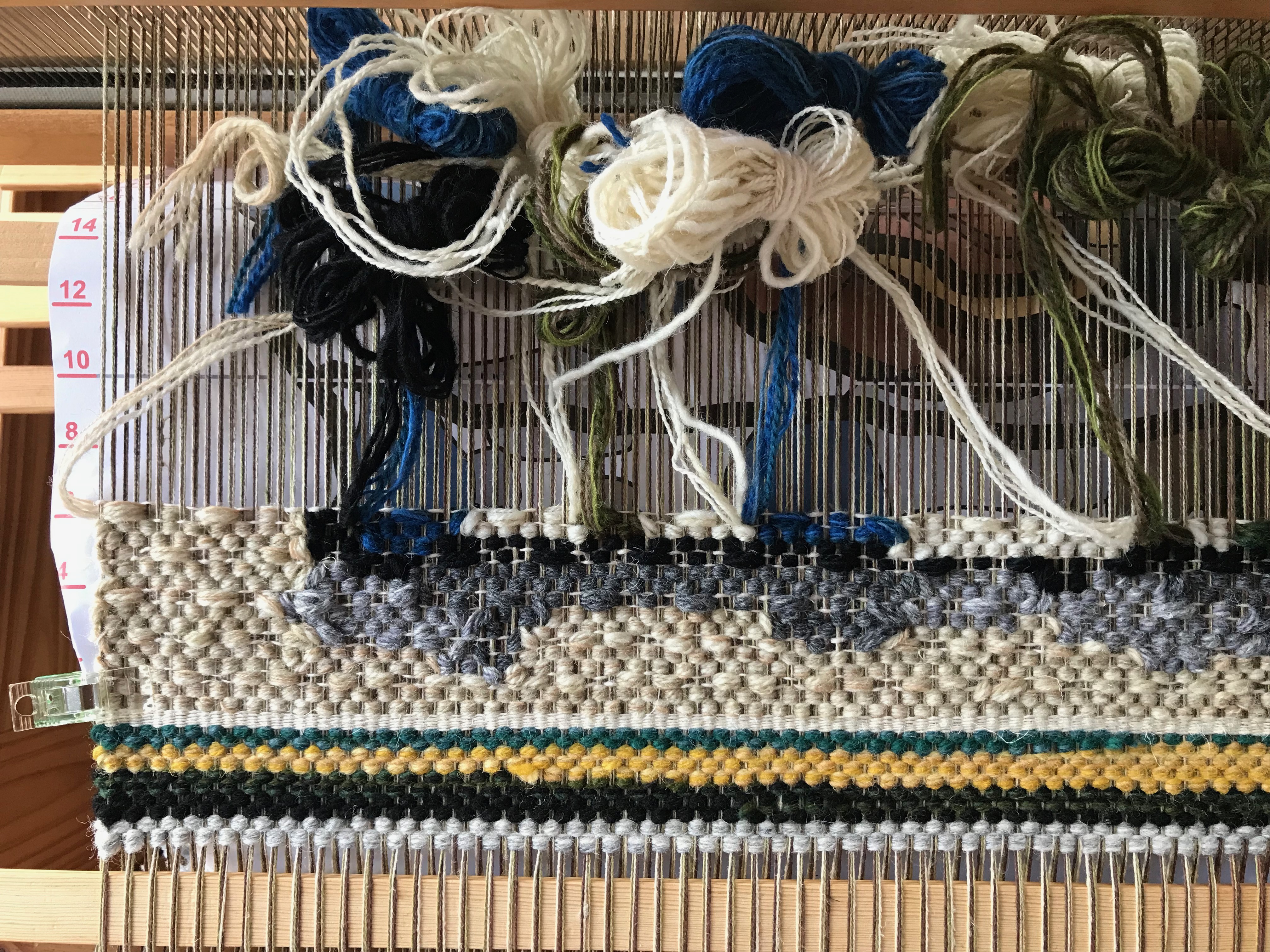
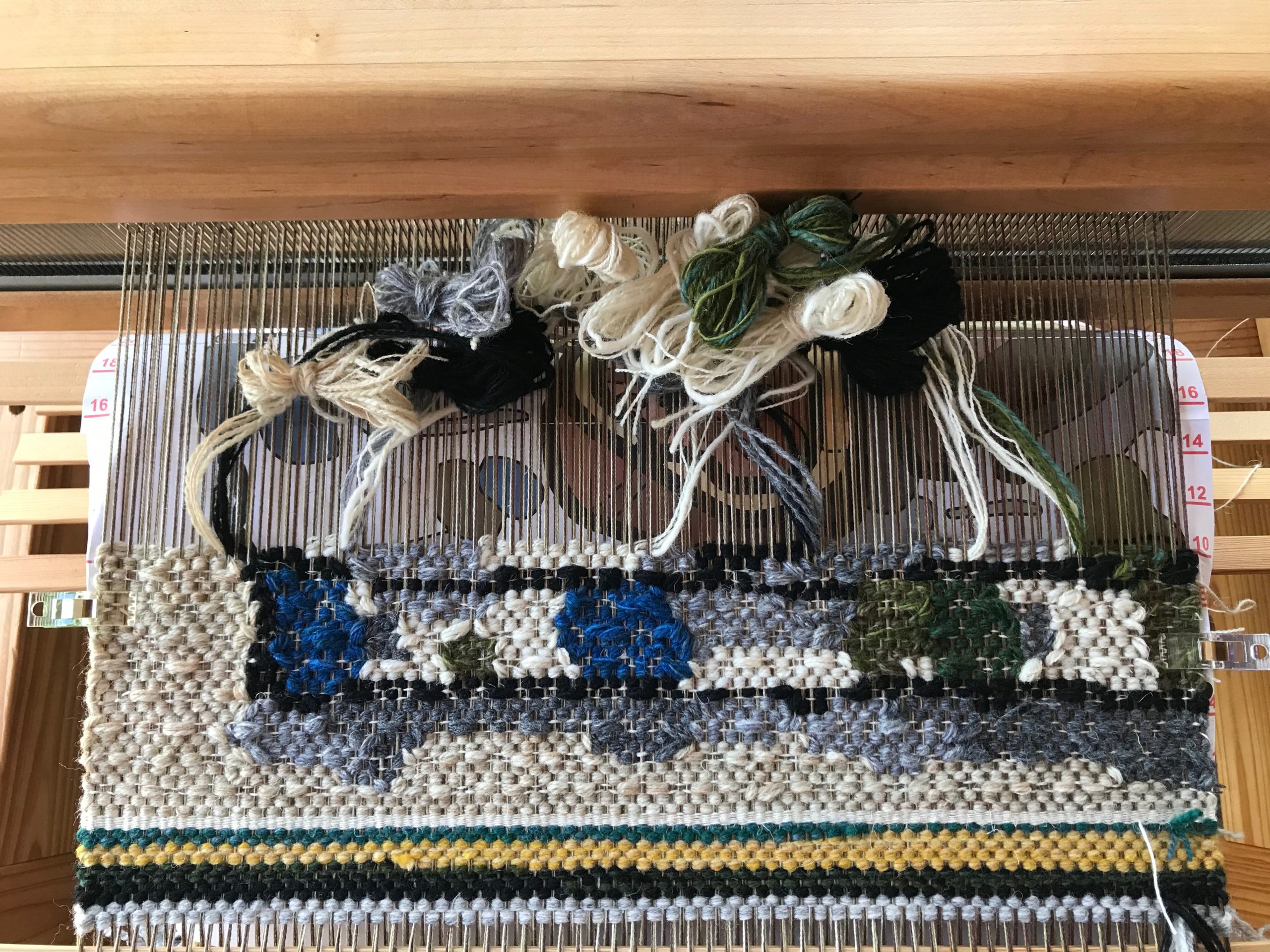
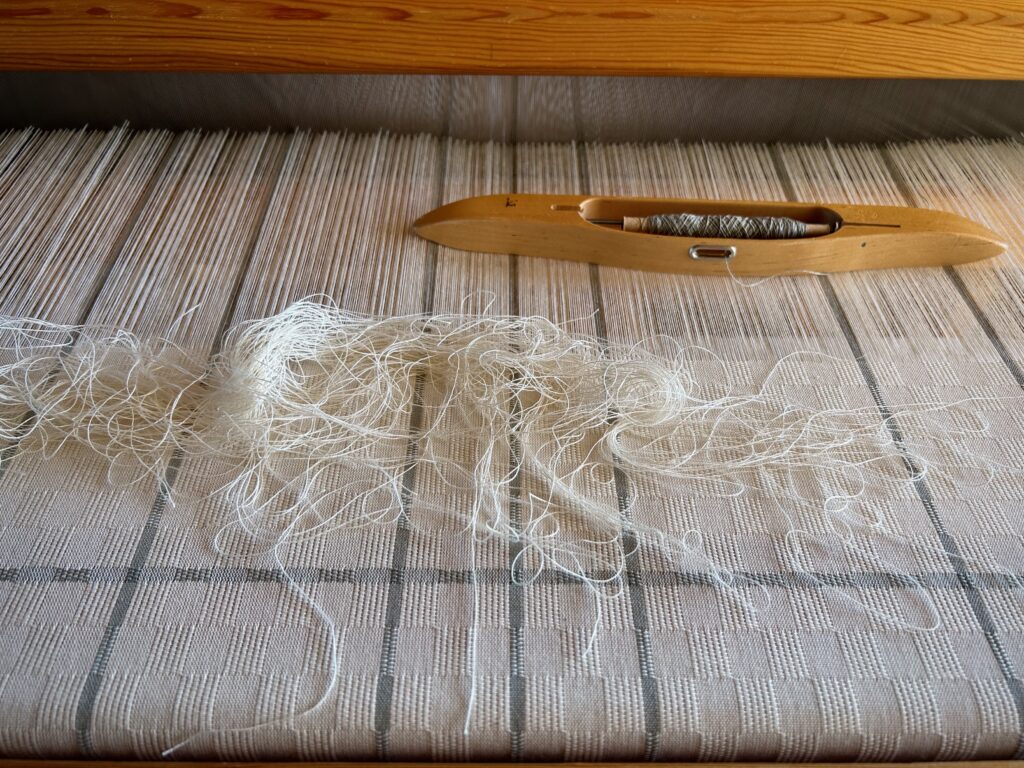
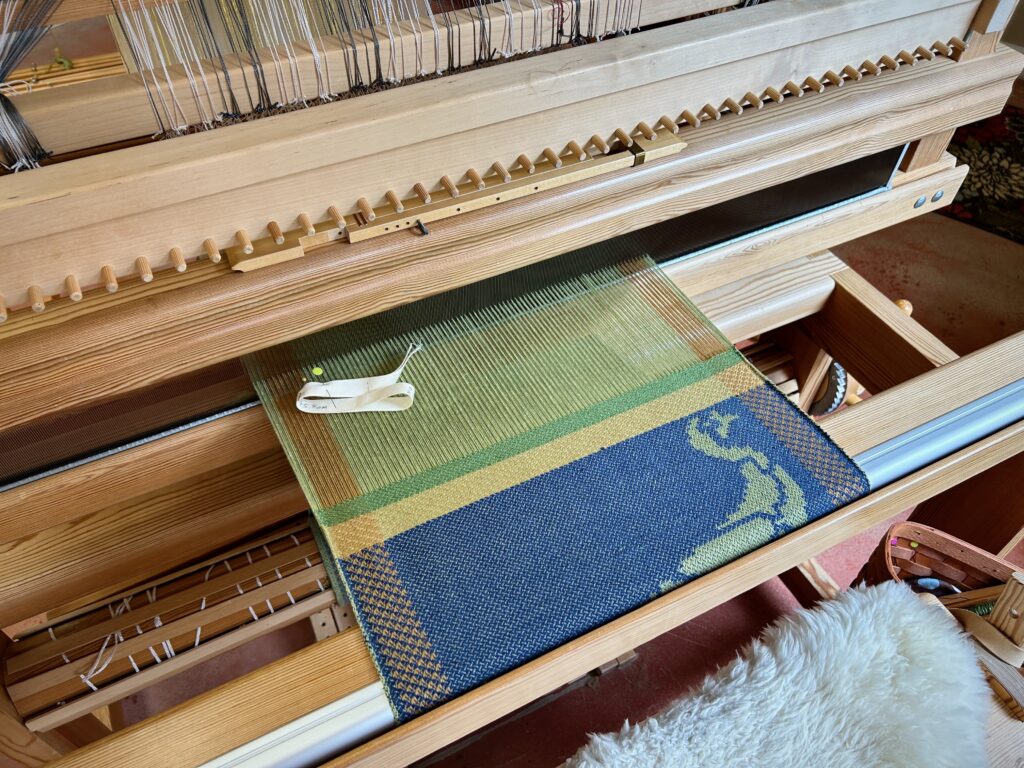
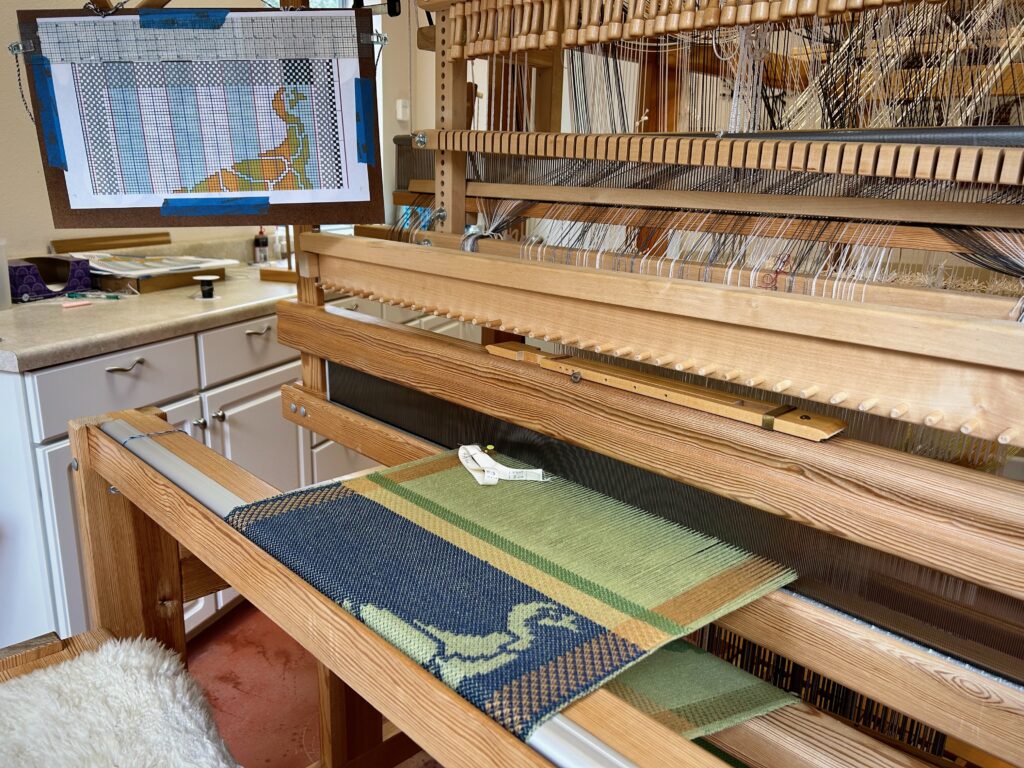
Every now and then I forget where I left off. This happens when I get interrupted when I am not quite finished with a sequence at the end of a weaving session, or when I get interrupted when I am just getting started back on the loom. Often, the interruptions are my own thoughts going in different directions. The only loss is a few dozen weft threads that get pulled out one by one, plus the time it takes to pull them out and weave the right ones back in. Everything is fixable.



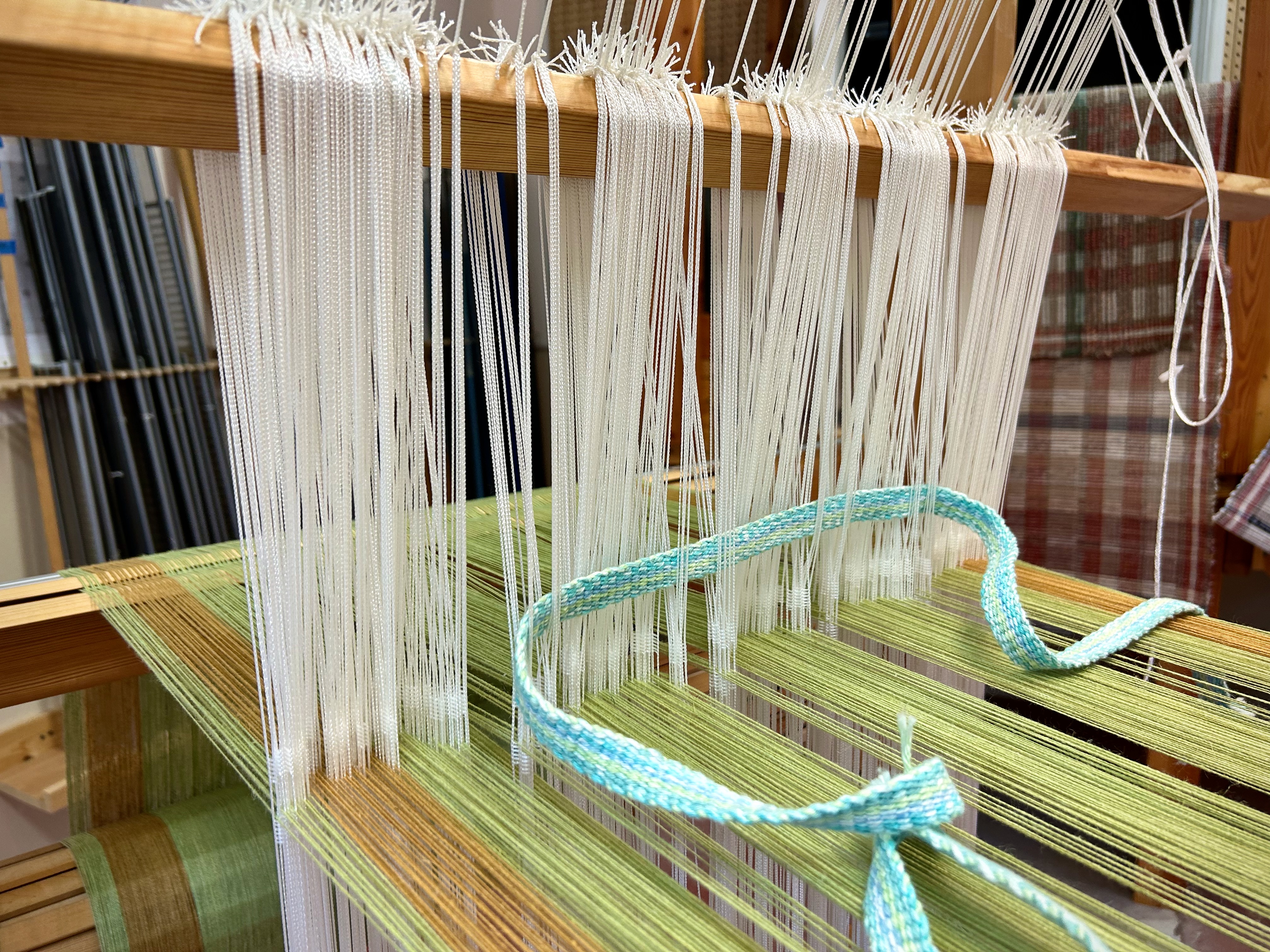
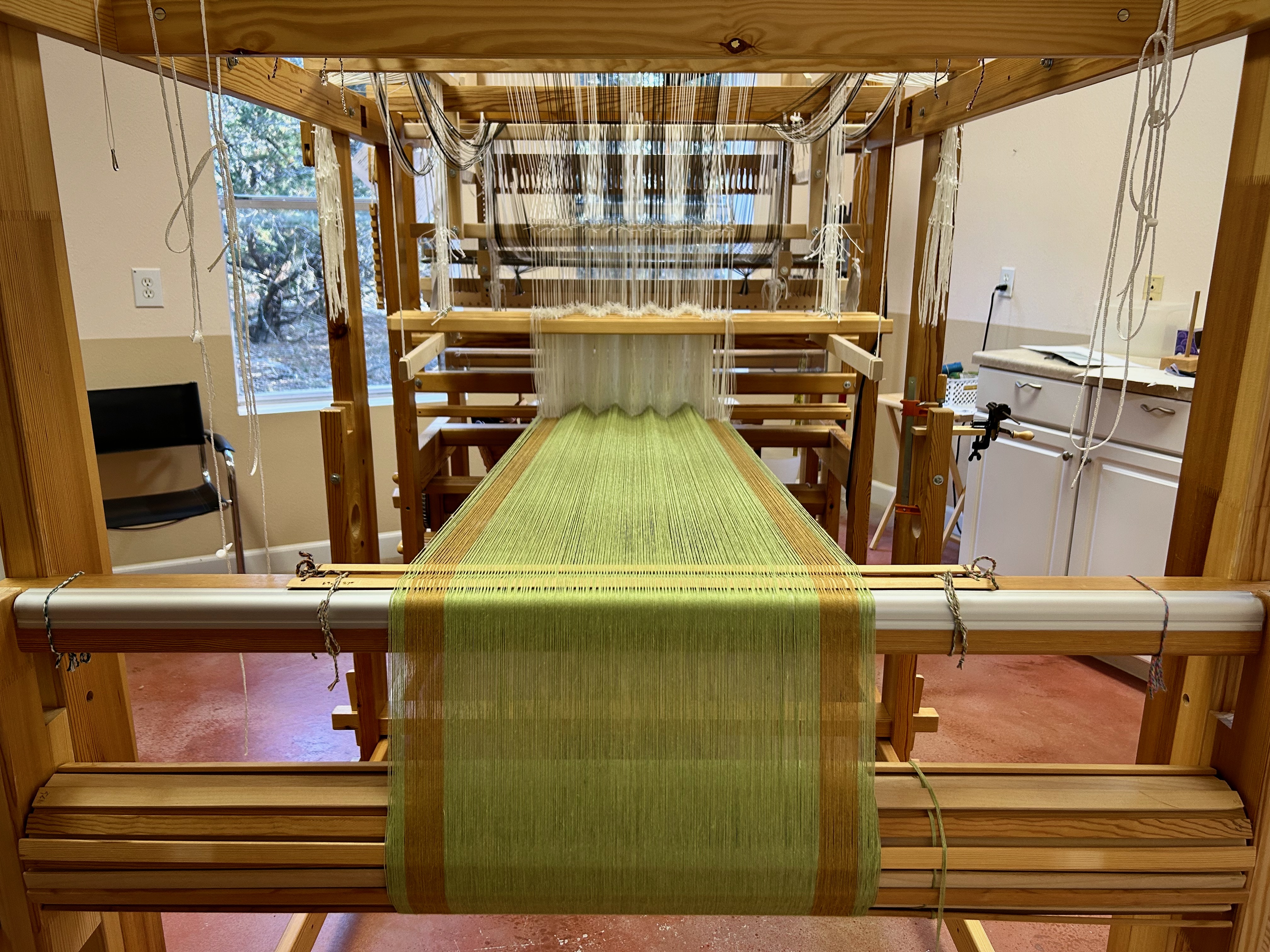
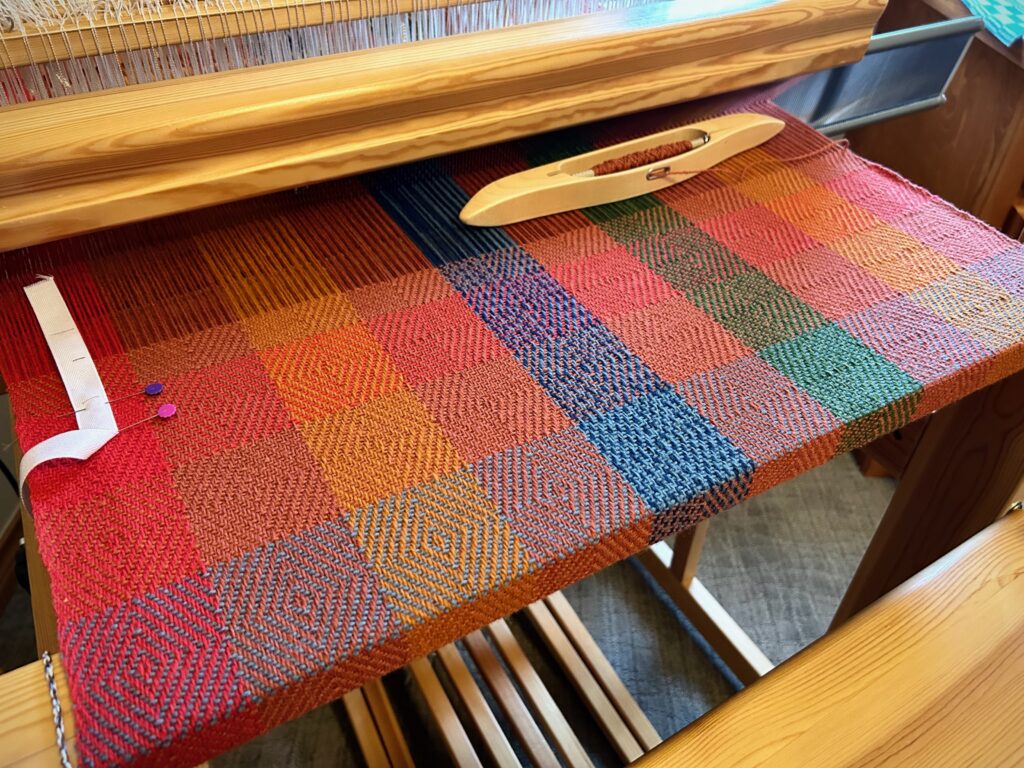
I have come to the unfortunate realization that I am probably short on blue weft yarn and green weft yarn. This project is using yarn from my excess, and the warp yarn was measured out just so. I miscalculated on the weft yarn. My solution is to space the blue and the green weft stripes further apart. If I still run out of either color I will finish with the colors I do have. I may end up liking it better that way. Everything is fixable.
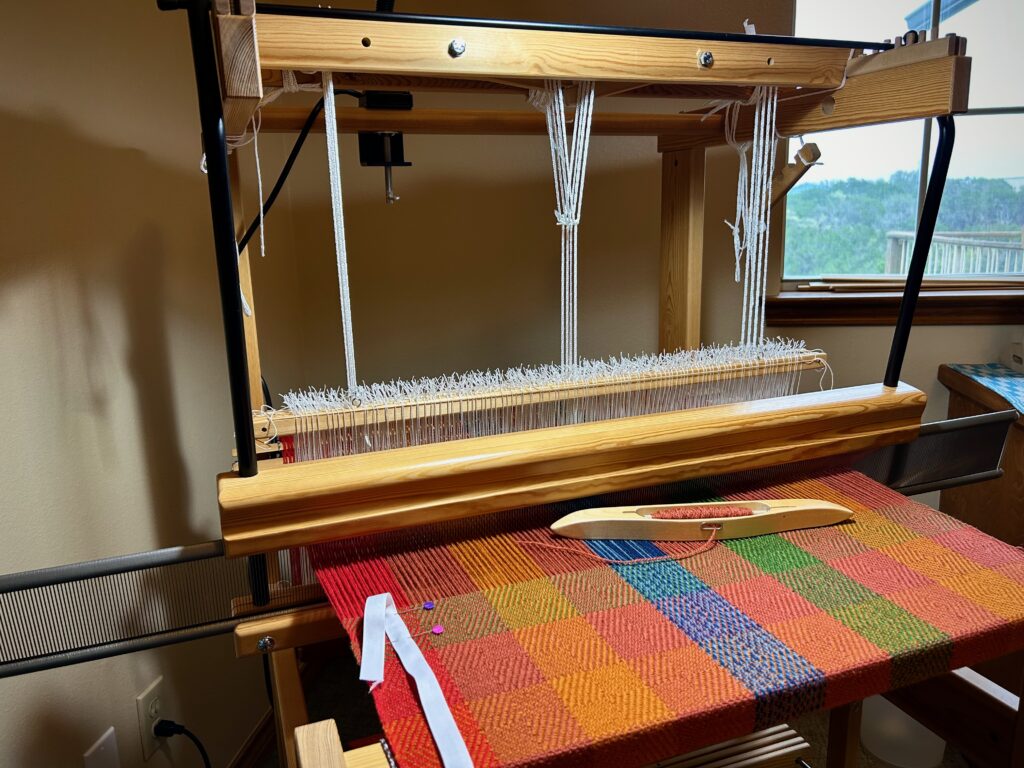



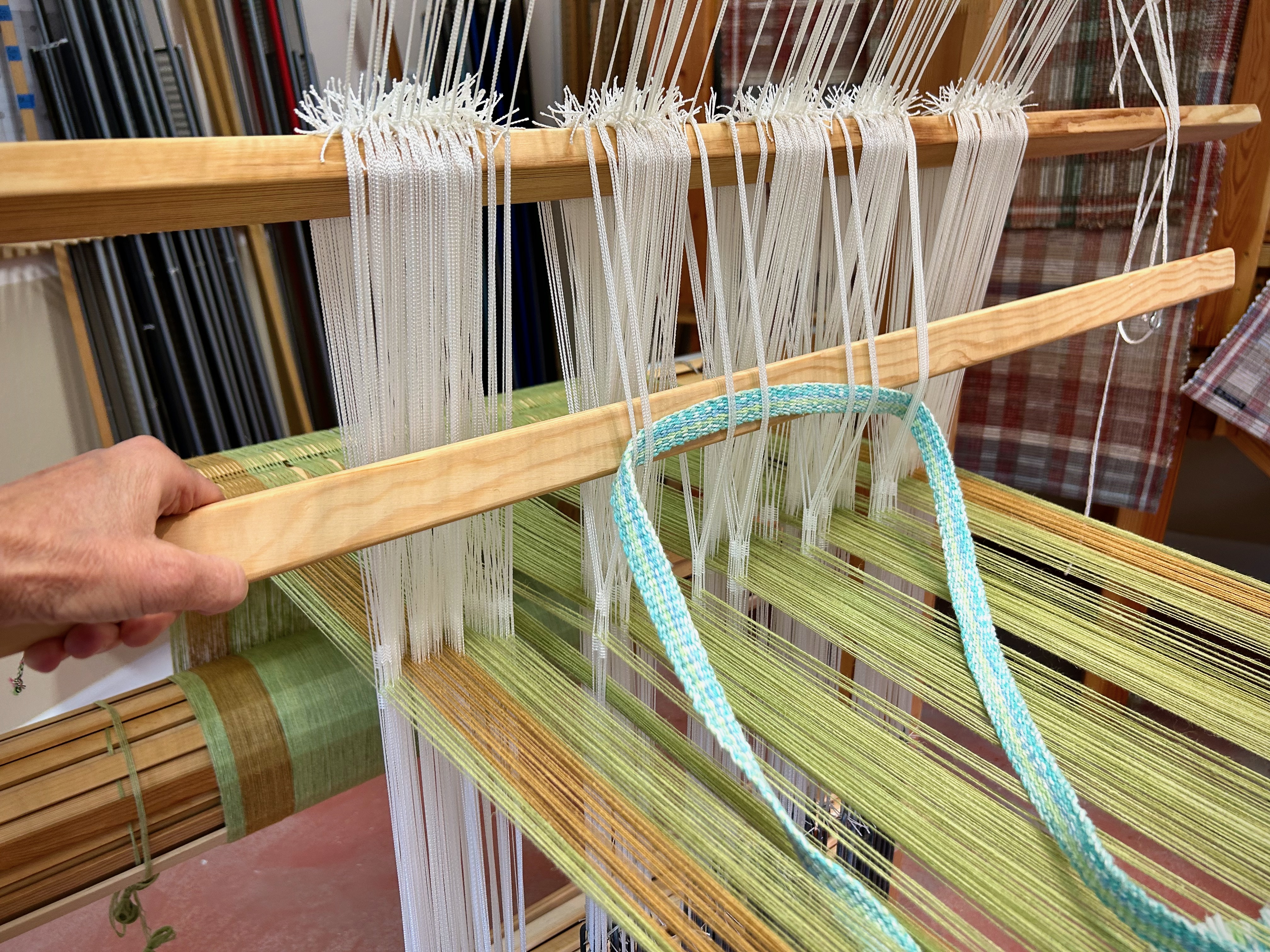
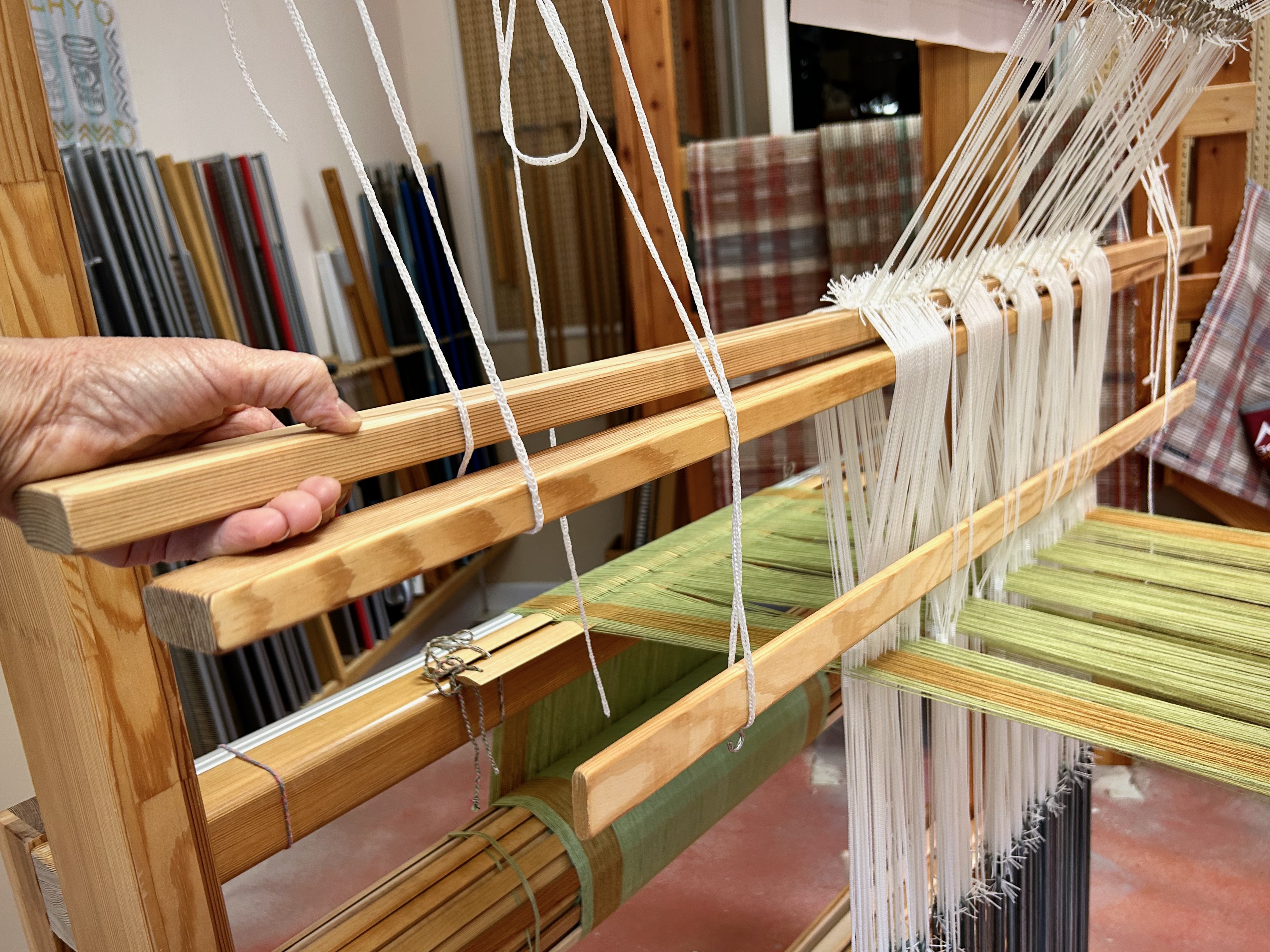
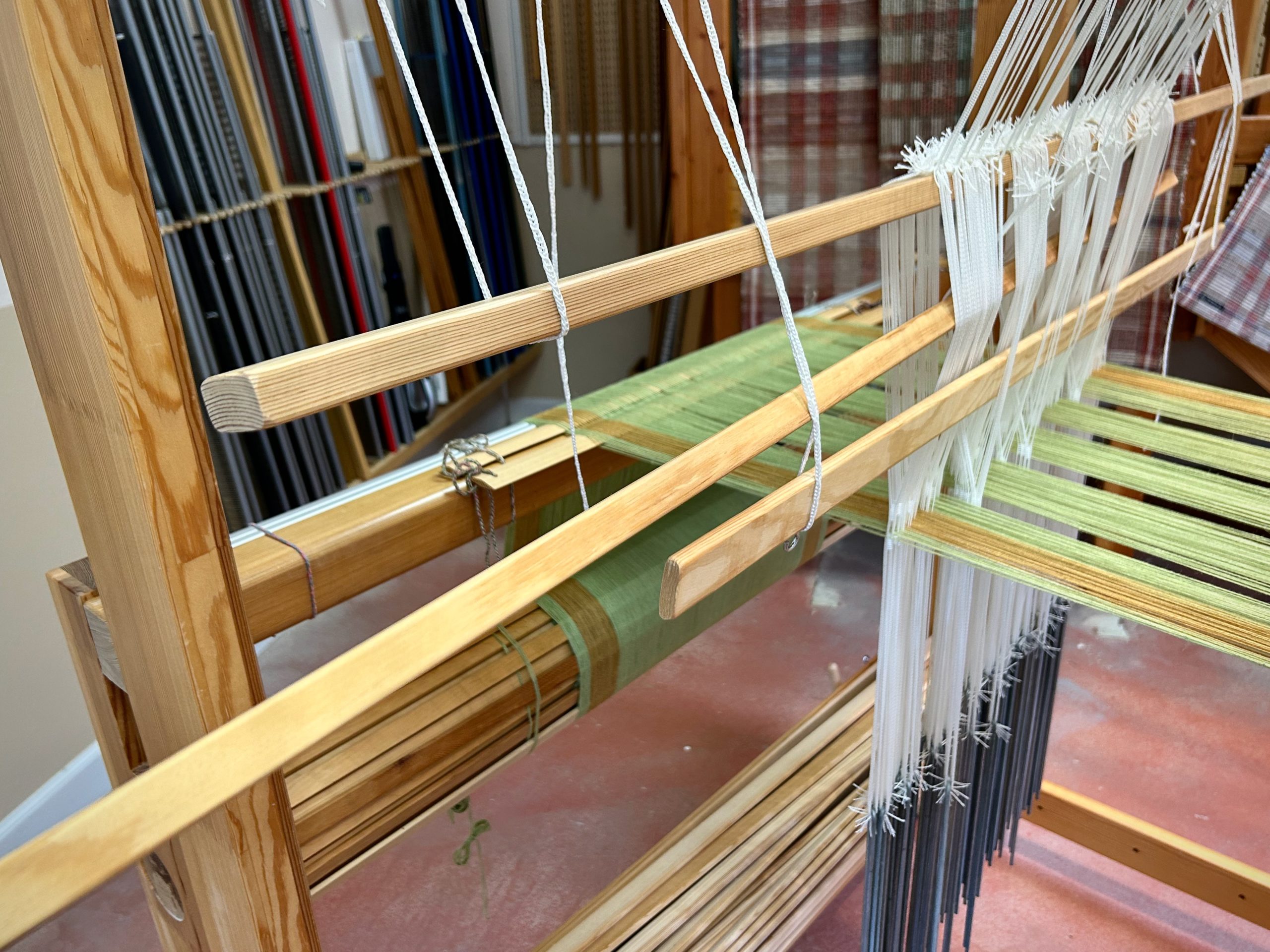
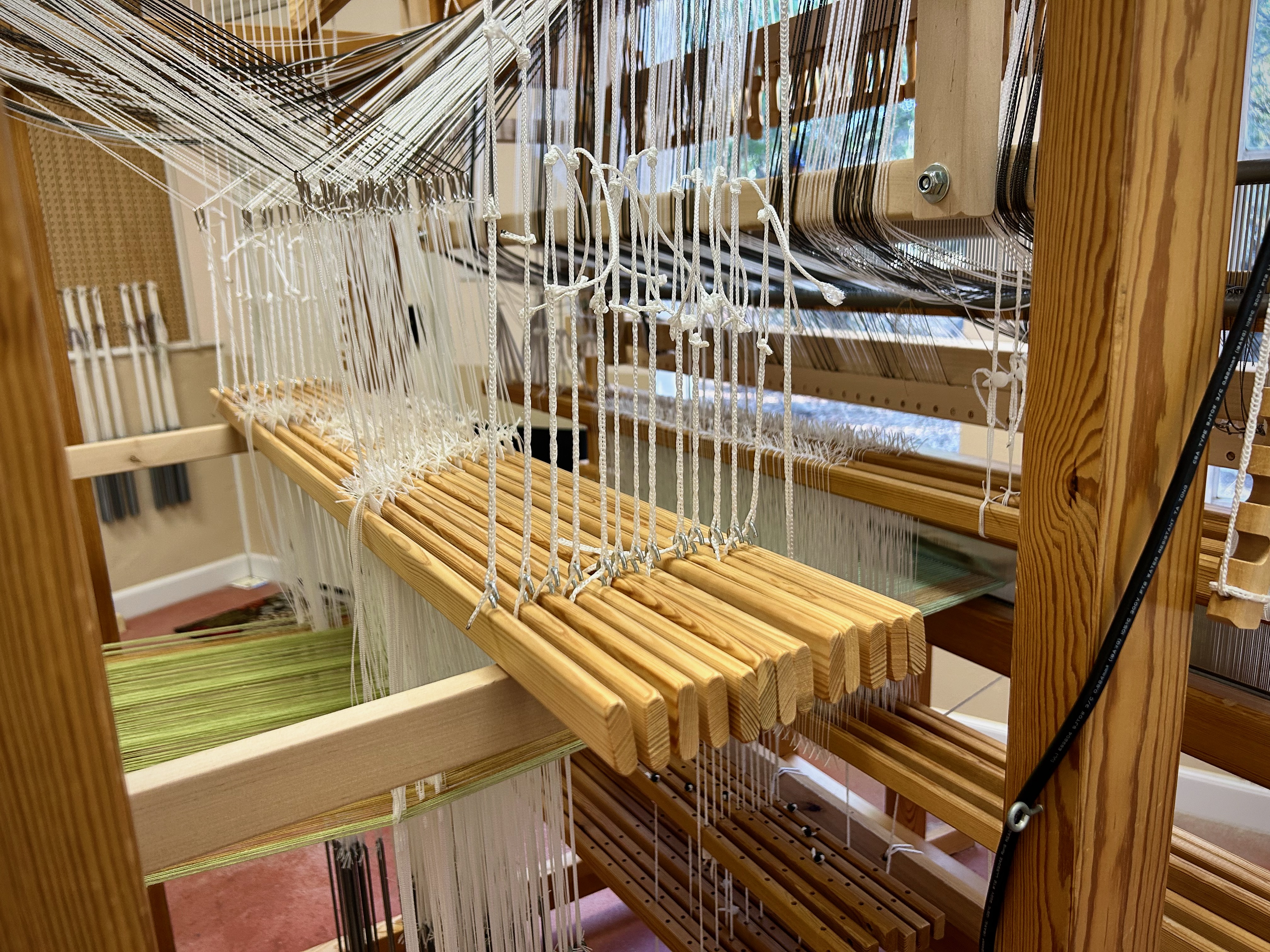
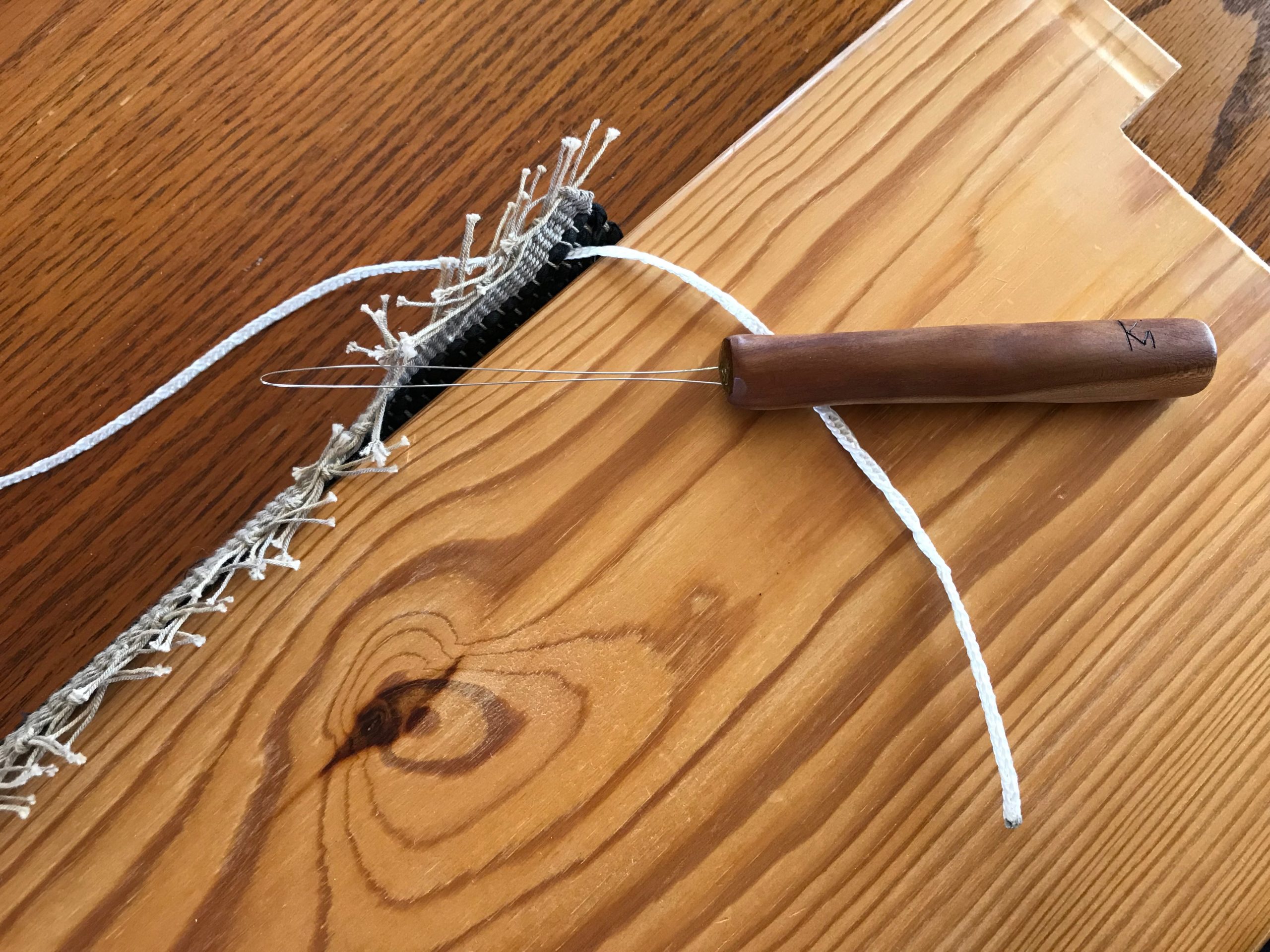
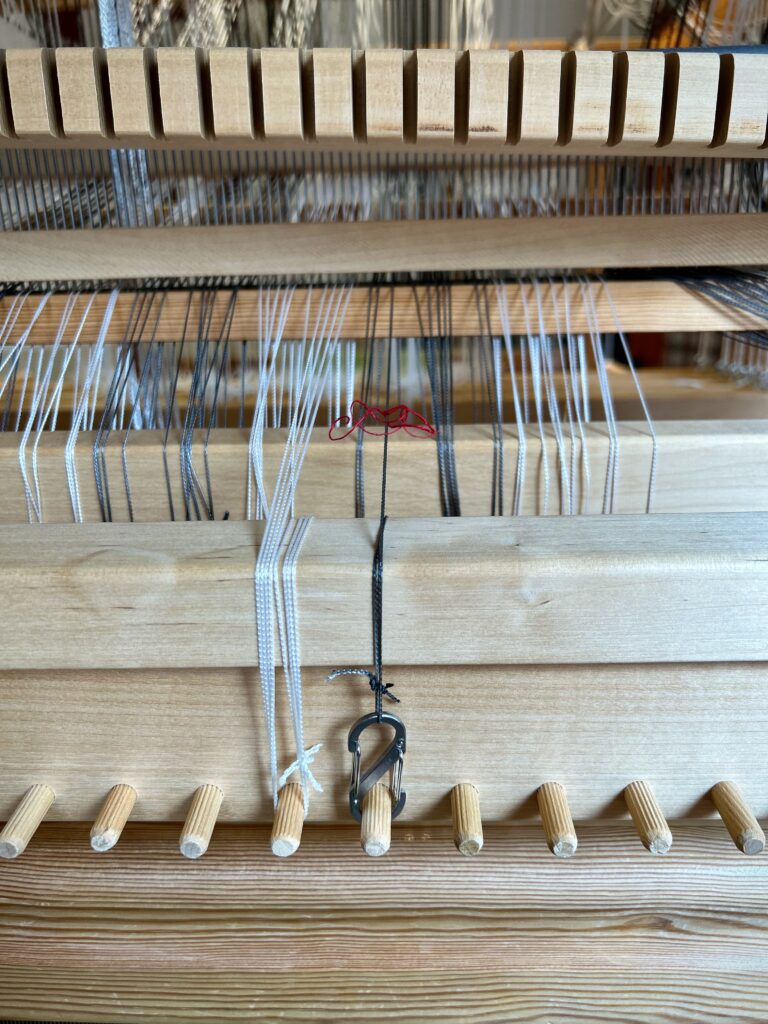
I did not imagine that one of the single-unit draw cords on the drawloom could snap in two while I am putting it on the hook bar. But it happened! Now what? I’m able to finish the 6-thread unit by tying a knot and maneuvering threads this way and that way. This is not acceptable for weaving the rest of the warp, however, nor even for the rest of this napkin. I just so happen to have a fancy clip that Steve brought to me a couple weeks ago, saying, “I thought you might be able to use this somewhere.” It is the perfect temporary fix for this shortened draw cord. I will replace the broken draw cord before starting the next critter napkin (roadrunner). Everything is fixable.
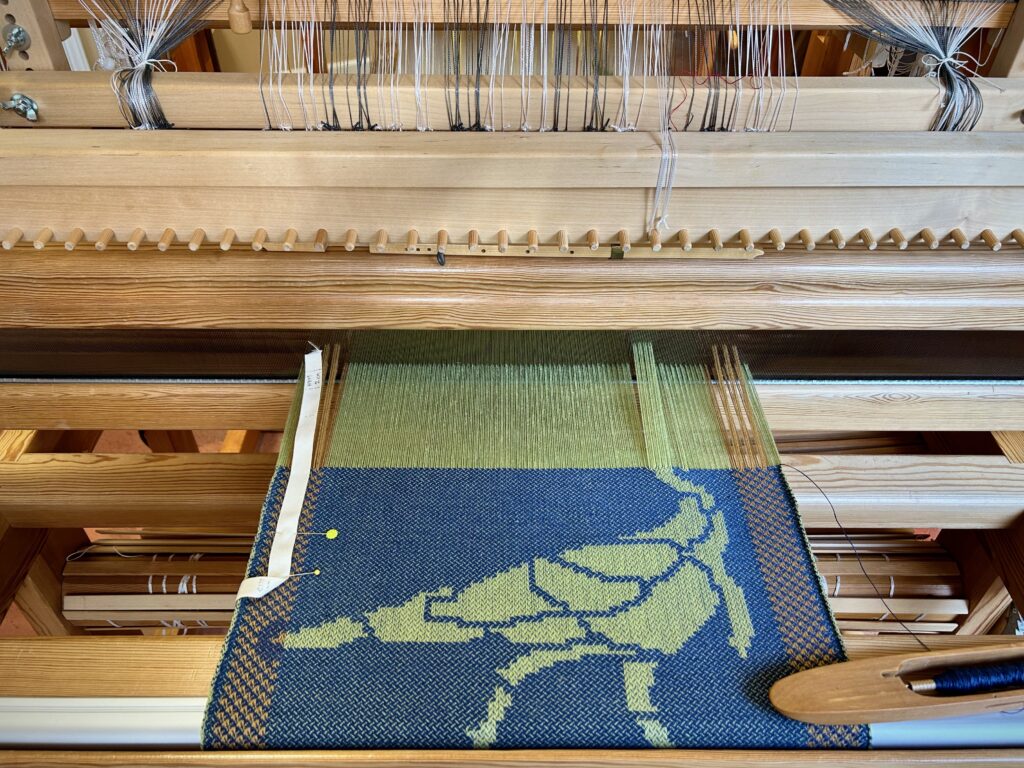




Yesterday we enjoyed Easter, the day of celebrating the resurrection of Jesus Christ from the dead. We are lost without Him, suffering from our own errors, miscalculations, and brokenness. The Heavenly Father raised Jesus from the dead to prove to us that Jesus is Lord. Everything is fixable in Him.
May you find the solution you need.
Your weaving friend, Karen